PTSD, or post-traumatic stress disorder, is a mental health condition that can have a significant impact on an individual’s well-being. It often occurs after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, and its symptoms can be debilitating. However, there is hope for recovery. Through the utilization of high-end therapies, individuals can regain their mental health and well-being and overcome the challenges of PTSD.
In this article, I will explore the most effective high-end therapies for PTSD recovery. These therapies are backed by research and have proven to be invaluable in helping individuals manage their symptoms, restore their quality of life, and find healing. By understanding and utilizing these therapies, individuals can embark on a journey of recovery and experience a renewed sense of hope and well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- High-end therapies offer hope and effective solutions for individuals seeking PTSD recovery.
- By understanding and utilizing these therapies, individuals can regain their mental health and well-being.
- These therapies are backed by research and have proven to be invaluable in managing symptoms and finding healing.
- PTSD recovery is possible, and individuals should never lose sight of the hope and support available to them.
- Through high-end therapies, individuals can overcome the challenges of PTSD and experience a renewed sense of hope and well-being.
Understanding PTSD and the Importance of Professional Treatment
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is often wrongly perceived as an untreatable condition. However, research has shown that effective therapies can significantly improve symptoms and support individuals on their path to recovery from PTSD. The importance of seeking professional treatment cannot be overstated.
The Misconception of PTSD as Untreatable
Contrary to popular belief, PTSD is a condition that can be effectively treated. With the right interventions and support, individuals with PTSD can attain significant improvements in their well-being and quality of life. Professional treatment plays a crucial role in addressing the complex nature of PTSD and guiding individuals towards lasting recovery.
Guided Care by Experienced Mental Health Professionals
When it comes to treating PTSD, the expertise and guidance of mental health professionals are invaluable. These professionals possess the knowledge and skills to understand the unique challenges individuals with PTSD face, allowing them to provide tailored, evidence-based interventions. By working closely with qualified professionals, individuals can receive the most appropriate and comprehensive care for their condition.
Building Personalized Treatment Plans
Personalization is key in PTSD treatment. Mental health professionals create personalized treatment plans that address the specific needs and circumstances of each individual. These plans may incorporate a combination of therapy modalities, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), cognitive processing therapy (CPT), prolonged exposure therapy (PE), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and medication management. By tailoring treatment to individual needs, professionals maximize the potential for successful outcomes.
Demystifying Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for PTSD
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a widely used and highly effective therapy for individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It focuses on identifying and changing unhelpful thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to PTSD symptoms. Through CBT, individuals learn new coping strategies and techniques to manage their symptoms and regain control over their lives.
How CBT Alters Unhelpful Thought Patterns
CBT works by helping individuals identify and challenge negative and distorted thoughts related to their traumatic experiences. It teaches them to recognize unhelpful thought patterns, such as catastrophizing, black-and-white thinking, and self-blame, and replace them with more realistic and adaptive thoughts. By addressing and altering these thought patterns, CBT aims to reduce the intensity and frequency of PTSD symptoms.
The APA’s Stance on CBT for PTSD Recovery
The American Psychological Association (APA) strongly supports the use of CBT as a treatment for PTSD recovery. According to the APA, CBT has a substantial evidence base and is considered one of the most effective therapies for PTSD. It is recommended as a first-line treatment by many mental health professionals, as it provides individuals with practical tools and strategies to manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
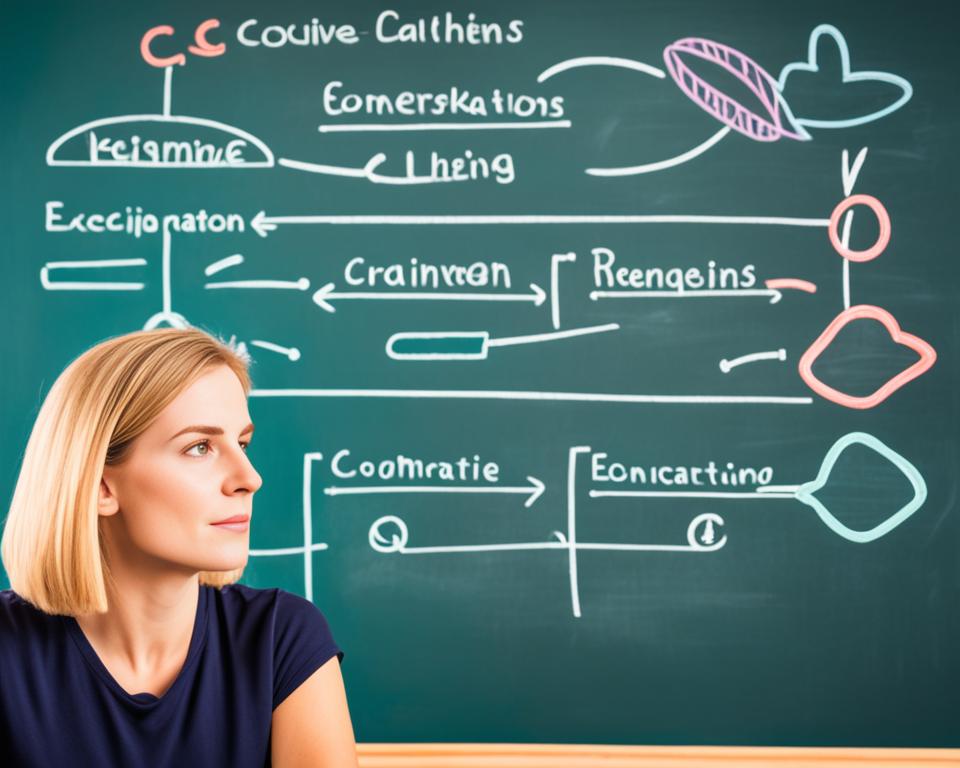

| Key Benefits of CBT for PTSD |
|---|
| 1. Helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns |
| 2. Teaches coping strategies to manage PTSD symptoms |
| 3. Empowers individuals to regain control over their lives |
| 4. Provides practical tools to improve daily functioning |
| 5. Reduces the intensity and frequency of PTSD symptoms |
The Role of Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) in Healing Trauma
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT) is a specific type of cognitive behavioral therapy that plays a crucial role in healing trauma, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) recovery. By challenging and reframing distorted thoughts and beliefs about the traumatic event, CPT helps individuals process and make sense of their trauma in a safe and structured environment. Through this process, the impact of the trauma on their daily lives can be reduced, and healing can begin.
CPT is grounded in the understanding that trauma often distorts an individual’s cognitive processing, leading to negative thoughts and beliefs about oneself, others, and the world. By addressing these distortions, CPT aims to help individuals regain control over their thoughts and emotions, ultimately promoting healing and recovery.
“Cognitive processing therapy has been shown to be an effective treatment for trauma-related conditions, including PTSD. By challenging and changing unhelpful thought patterns, individuals can take control of their recovery journey and find healing.”
During CPT sessions, individuals work closely with a trained therapist to identify and examine the thoughts and beliefs that have developed as a result of the traumatic experience. These thoughts and beliefs are then challenged using various cognitive techniques. Through this process, individuals gain a deeper understanding of how the trauma has affected their thinking and gain the tools to reframe these thoughts in a more adaptive and realistic way.
In addition to addressing distorted thoughts and beliefs, CPT also focuses on teaching individuals healthy coping strategies and skills to manage their symptoms. This can include developing effective stress management techniques, improving problem-solving abilities, and enhancing communication skills.
CPT typically consists of a structured treatment plan that involves multiple sessions spread over a set period of time. The duration of treatment can vary depending on the individual’s needs and progress. However, research has shown that individuals who undergo CPT often experience significant improvements in their trauma symptoms and overall well-being.
In summary, cognitive processing therapy (CPT) plays a vital role in healing trauma and promoting PTSD recovery. By challenging distorted thoughts and beliefs, individuals can gain a new perspective on their traumatic experiences and find healing. With the guidance of a trained therapist, individuals can develop healthy coping strategies and skills to manage their symptoms and regain control over their lives.
Progressing with Prolonged Exposure Therapy (PE)
Prolonged exposure therapy (PE) is an evidence-based treatment for individuals with PTSD. It has shown significant effectiveness in helping individuals overcome the debilitating symptoms associated with trauma. PE involves a structured approach to gradually confronting and exposing oneself to memories, feelings, and situations that have been avoided due to the traumatic event.
The key component of PE is gradual exposure. By systematically and repeatedly exposing oneself to the distressing memories and triggers, individuals can reduce their avoidance and develop a sense of mastery over their traumatic experiences. This exposure is conducted under the guidance of a trained mental health professional, ensuring safety and support throughout the process.
Through the process of gradual exposure, individuals learn to confront their fears and develop healthier coping mechanisms to manage their anxiety. By facing and processing the traumatic memories in a controlled and therapeutic environment, the distress associated with those memories diminishes over time.
One of the significant benefits of PE is its impact on daily functioning. Avoidance behaviors, a common symptom of PTSD, can severely disrupt an individual’s ability to navigate everyday life. Through prolonged exposure, individuals can regain control over their lives and engage in activities they once avoided due to their trauma.
PE has been shown to improve daily functioning and quality of life for individuals with PTSD. By confronting avoidance behaviors and gradually exposing oneself to the traumatic memories, individuals can reduce the distress and anxiety associated with those memories, ultimately reclaiming their ability to live a fulfilling life.
Incorporating prolonged exposure therapy into a comprehensive treatment plan for PTSD can be a transformative experience for individuals seeking to overcome the impact of trauma and move towards recovery.

| Benefits of Prolonged Exposure Therapy (PE) |
|---|
| Reduces avoidance behaviors |
| Diminishes distress associated with traumatic memories |
| Improves daily functioning |
| Enhances quality of life |
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) as a Unique Approach
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a therapy specifically designed to address traumatic memories and experiences in individuals with PTSD. This unique approach utilizes a series of eye movements or other bilateral stimulation techniques to reprocess and reduce the distress associated with these traumatic memories.
During an EMDR session, the therapist guides the client through controlled eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation, such as tapping or auditory cues. This bilateral stimulation is believed to activate the brain’s natural healing mechanisms, allowing the individual to reprocess and integrate traumatic memories in a safe and therapeutic manner.
EMDR is based on the Adaptive Information Processing (AIP) model, which suggests that traumatic experiences can become “stuck” in the brain’s memory networks, contributing to the development of PTSD symptoms. By engaging in bilateral stimulation, EMDR aims to facilitate the reprocessing of these memories, allowing for their integration into a healthier and more adaptive memory network.
“EMDR not only helps individuals process traumatic memories, but it also aims to transform these memories, reducing their emotional charge and allowing individuals to move forward in their recovery journey.” – Dr. Emily Wilson, Licensed Psychologist
One of the unique aspects of EMDR is its focus on both the traumatic memories and the individual’s present-day experience. By integrating the past traumatic events with the present reality, EMDR helps individuals develop new, more positive beliefs about themselves and their abilities to cope with stress and adversity.
EMDR is recognized as an evidence-based therapy for PTSD by organizations such as the American Psychiatric Association and the World Health Organization. It has been extensively researched and has shown promising results in reducing PTSD symptoms and promoting overall well-being.
Overall, EMDR offers a unique and effective approach to PTSD treatment, utilizing eye movements or other bilateral stimulation techniques to reprocess traumatic memories and promote healing. This therapy can be a valuable tool in the recovery journey, allowing individuals to address and overcome the impact of their traumatic experiences.
Integrating Medications into PTSD Treatment
Medications can be a valuable component of PTSD treatment, working in conjunction with therapy to help manage symptoms and support individuals on their path to recovery. One class of medications that has shown promise in providing relief from PTSD symptoms is selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). These FDA-approved drugs, such as sertraline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil), are commonly prescribed to address symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other associated conditions that often accompany PTSD.

SSRIs function by increasing the availability of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in mood regulation, in the brain. By rebalancing serotonin levels, these medications can help alleviate feelings of sadness, anxiety, and distress commonly experienced by individuals with PTSD.
It is essential to note that while SSRIs are FDA-approved for PTSD symptom relief, the effectiveness of these medications can vary from person to person. Therefore, close monitoring and regular communication with a healthcare professional are crucial to determine the appropriate dosage and assess the medication’s efficacy.
In some cases, off-label medication use may be considered as part of a comprehensive PTSD treatment plan. Off-label use involves prescribing a medication for a purpose other than its FDA-approved indication. Healthcare providers may explore off-label options to address specific symptoms or individual needs that may not be adequately managed by FDA-approved treatments alone. This approach allows for a more personalized and tailored treatment approach, taking into account the unique challenges and circumstances of the individual.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional who specializes in PTSD care to ensure the safe and effective integration of medications into the overall treatment plan. A comprehensive approach combining therapy, medication, and other supportive interventions can offer individuals the best chance for successful PTSD symptom management and long-term recovery.
Trauma-Focused Therapies: The Current Gold Standard
Trauma-focused therapies are considered the gold standard in treating PTSD. These therapies have been extensively researched and shown to be effective in reducing PTSD symptoms and improving overall well-being. By addressing the specific impact of trauma on an individual, these therapies provide targeted and comprehensive support for PTSD recovery.
Evidence-Based Practices and Their Effectiveness
Evidence-based practices are the cornerstone of trauma-focused therapies for PTSD treatment. These practices are grounded in empirical research and have been proven to be effective in clinical studies. Therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), cognitive processing therapy (CPT), prolonged exposure therapy (PE), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and other specialized trauma therapies incorporate evidence-based techniques and interventions to provide the most beneficial outcomes for individuals with PTSD.
Combating PTSD with Specialized Trauma Therapies
Specialized trauma therapies target the unique needs and experiences of individuals affected by PTSD. These therapies focus on specific aspects of trauma and tailor treatment approaches accordingly. For example, cognitive processing therapy (CPT) emphasizes challenging and reframing distorted thoughts and beliefs about the traumatic event, while prolonged exposure therapy (PE) aims to gradually expose individuals to avoided traumatic memories and situations. Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) uses eye movements or other bilateral stimulation techniques to reprocess and reduce the distress associated with traumatic memories. By utilizing these specialized approaches, trauma-focused therapies can address the complex nature of PTSD and promote healing and recovery.
Retracing the Evolution of PTSD Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis and treatment of PTSD have evolved over time as our understanding of trauma and its impact on mental health has deepened. From the observations of early physicians like Joseph Auenbrugger to the current diagnostic criteria outlined in the DSM-V, the recognition and treatment of PTSD have undergone significant changes. This section will explore the historical context and milestones in the development of PTSD diagnosis and PTSD treatment.
The understanding of PTSD has evolved throughout history, with major advancements in diagnosing and treating the condition. Early physicians recognized the symptoms of trauma but lacked a comprehensive understanding of the underlying mechanisms. It was not until the mid-20th century that PTSD started to gain recognition as a distinct diagnosis.
“The concept of PTSD emerged after World War I, when it was initially called ‘shell shock’ or ‘combat fatigue.’ These terms described the psychological distress experienced by soldiers exposed to the horrors of war. However, it was not until the Vietnam War that PTSD gained official recognition as a mental health disorder.”
The evolution of PTSD diagnosis and treatment continued with advancements in psychology and psychiatry. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) played a significant role in standardizing the diagnostic criteria for PTSD. The DSM-III, published in 1980, included PTSD as a distinct diagnosis for the first time. Subsequent revisions, such as the DSM-V, have refined and expanded the diagnostic criteria to better capture the varied manifestations of the condition.
The treatment of PTSD has also evolved over time, moving away from approaches that focused solely on symptom suppression to ones that promote long-term recovery. Early treatment methods primarily relied on medication, while talk therapies started gaining prominence in the 20th century. Today, evidence-based therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and prolonged exposure therapy (PE) are commonly used to treat PTSD.
The evolution of PTSD diagnosis and treatment demonstrates our commitment to understanding and addressing the complex nature of trauma and its impact on mental health. By continuously building upon our knowledge and refining our approaches, we can provide more effective and comprehensive care for individuals with PTSD.
| Year | Key Milestones in PTSD Diagnosis and Treatment |
|---|---|
| 1914-1918 | Recognition of psychological distress in soldiers during World War I, referred to as “shell shock.” |
| 1952 | Inclusion of “gross stress reaction” in the first edition of the DSM. |
| 1980 | Inclusion of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as a distinct diagnosis in the DSM-III. |
| 1994 | Introduction of a “traumatic event” criterion in the DSM-IV. |
| 2013 | Revisions in the DSM-5, including clarification of symptoms, subtypes, and criteria for diagnosis. |
Exploring the Three Main Goals of PTSD Therapy
PTSD therapy aims to achieve three main goals: addressing symptoms and improving the quality of life, acquiring skills for emotional regulation, and promoting overall well-being. By targeting symptoms, therapy helps individuals manage distressing experiences and regain control over their lives. It also focuses on equipping individuals with the necessary skills to regulate their emotions and navigate their daily lives effectively.
Addressing symptoms and improving the quality of life is a fundamental aspect of PTSD therapy. Therapists work closely with individuals to identify and reduce the impact of PTSD symptoms such as intrusive memories, hypervigilance, and avoidance behaviors. By addressing these symptoms head-on, therapy helps individuals regain a sense of control and improve their overall well-being.
Another key goal of PTSD therapy is the acquisition of skills for emotional regulation. Traumatic experiences can often disrupt an individual’s ability to manage their emotions, leading to heightened reactivity, anger, and mood swings. Therapy helps individuals develop effective coping mechanisms and techniques to regulate their emotions, allowing them to navigate daily life with greater stability.
Finally, PTSD therapy focuses on promoting overall well-being. This includes enhancing self-care practices, fostering healthy relationships and support systems, and improving the individual’s quality of life. By addressing all these aspects, therapy aims to help individuals not just recover from PTSD, but also thrive in their lives and experience a higher level of well-being.
Empowering Self-Care: Techniques for Long-Term PTSD Management
Self-care is a crucial component of long-term PTSD management and plays a significant role in sustaining mental wellness. Incorporating self-management strategies, including mindfulness techniques and stress management practices, into daily life can greatly support the healing journey. These self-care practices are essential for promoting self-empowerment, resilience, and overall well-being.
Self-Management Strategies Including Mindfulness and Stress Management
One powerful technique for managing PTSD is mindfulness. Mindfulness involves being fully present in the moment, observing thoughts and feelings without judgment. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can cultivate greater awareness of their emotions and reactions, allowing for a more measured response to triggers and stressors. Additionally, relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can help reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm.
Stress management is another key aspect of self-care for individuals with PTSD. Developing healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress can be instrumental in maintaining mental wellness. Engaging in activities such as exercise, yoga, or meditation can help reduce stress hormones and promote a sense of well-being. It’s important to find activities that personally resonate and provide a sense of enjoyment or relaxation.
The Role of Self-Care Practices in Sustaining Mental Wellness
Self-care practices not only assist in managing PTSD symptoms but also play a significant role in sustaining overall mental wellness. Engaging in activities that bring joy, peace, and fulfillment can contribute to an improved quality of life. Taking time for self-reflection, pursuing hobbies, connecting with loved ones, and prioritizing rest and relaxation are all essential aspects of self-care.
By dedicating attention and energy to self-care practices, individuals with PTSD can empower themselves to take an active role in their own healing process. It’s crucial to remember that self-care is not selfish but an essential part of maintaining mental well-being and resilience.

Mental Health and Well-Being: Creating a Supportive Environment for PTSD Recovery
Creating a supportive environment is crucial for individuals with PTSD to promote their mental health and well-being. By fostering a culture of acceptance and understanding, we can reduce stigma and provide the necessary framework for individuals to seek help and engage in their recovery journey.
Increasing Mental Health Awareness and Reducing Stigma
One of the key aspects of creating a supportive environment for individuals with PTSD is increasing mental health awareness and reducing the stigma associated with seeking help. It is essential to educate the general public about the realities of PTSD and the impact it has on individuals’ lives. By promoting understanding and empathy, we can encourage open discussions and break down the barriers that prevent individuals from seeking the support they need.
“Mental health is just as important as physical health, and it’s time we treat it that way.” – Anonymous
We must challenge misconceptions and stereotypes surrounding PTSD and mental health. By sharing personal stories and lived experiences, we can humanize the condition and help others understand that seeking treatment is a sign of strength, not weakness. Through dialogue and education, we can create an environment where individuals with PTSD feel safe, supported, and understood.
Leveraging Mental Health Resources for Comprehensive Support
In addition to increasing awareness and reducing stigma, it is vital to leverage mental health resources to provide comprehensive support to individuals with PTSD. There is a wide range of resources available, including therapy services, support groups, helplines, and online platforms.
Therapy services, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), cognitive processing therapy (CPT), and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), can be highly effective in helping individuals manage and recover from PTSD. These evidence-based therapies provide individuals with the tools and strategies they need to address their symptoms and work towards healing.
Support groups offer a sense of community and connection for individuals with PTSD. Engaging with others who have had similar experiences can provide validation, support, and a safe space for sharing struggles and victories.
Helplines and online platforms provide accessible and immediate support for individuals in crisis or needing guidance. These resources offer a valuable lifeline for those who may be hesitant to seek in-person assistance or require immediate help outside of regular office hours.
By leveraging these mental health resources effectively, we can ensure that individuals with PTSD have access to the comprehensive support they need at different stages of their recovery journey. The availability and utilization of these resources can make a significant impact in promoting mental health and well-being.

| Resources | Description |
|---|---|
| Therapy Services | Professional therapies such as CBT, CPT, and EMDR |
| Support Groups | Community-based groups for shared experiences and support |
| Helplines | Phone lines for immediate crisis support and guidance |
| Online Platforms | Virtual resources providing a range of mental health support |
By embracing a supportive environment that promotes mental health awareness, reduces stigma surrounding PTSD, and provides comprehensive mental health resources, we can empower individuals with PTSD on their recovery journey. Together, we can create a society that prioritizes mental well-being and supports individuals in their pursuit of a healthier and fulfilling life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective high-end therapies are available for individuals seeking PTSD recovery. By understanding the importance of professional treatment, exploring evidence-based therapies, integrating medications when necessary, and prioritizing self-care, individuals can find the support and resources needed to reclaim their mental health and well-being. It is crucial to remember that recovery is possible, and with the right tools and support, individuals can overcome the challenges of PTSD and thrive in their lives.
